Innovation in education is more than a buzzword; it’s a driving force for change. It challenges old ways of teaching and learning and brings in new, more effective methods. Focusing on open innovation, we see a shift where teamwork and shared knowledge break traditional barriers in educational institutions. This method is not only about using new technologies; it’s about completely rethinking how we approach education to make it more welcoming, engaging, and connected.
In this article, we will explore how open innovation is actively reshaping higher education. This isn’t just a concept for discussion; it’s a practical approach to making real changes. We’ll look at how universities are collaborating on research, how course content is being developed with input from industry professionals, how students are leading their own innovative projects, and how access to educational materials is becoming more open and widespread. The influence of open innovation is significant and wide-ranging.
Understanding Innovation in Education
Innovation in education encompasses the adoption of new ideas, methods, or products that substantially enhance teaching, learning, and the management of education. This concept extends far beyond the realm of technology. It’s about introducing and implementing creative approaches that redefine curriculum design, teaching methodologies, and the entire educational experience.
Broadening the Scope Beyond Technology
While technology plays a significant role, innovation in education is not confined to digital tools or online platforms. It’s about a holistic reimagining of how education is delivered and received. This includes:
- Curriculum Design: Innovating in curriculum involves integrating interdisciplinary approaches, focusing on skills needed for the future, and aligning educational content with real-world challenges. It’s about creating a curriculum that is responsive to the changing demands of the job market and societal needs.
- Teaching Methods: Innovation in teaching methods can mean flipping the classroom, where students engage with lectures at home and do ‘homework’ in class, fostering more interaction and hands-on learning. It could also involve experiential learning, where students learn through experiences, or project-based learning, where students work on real-world projects.
- Assessment Techniques: Moving away from traditional exams and tests, innovative assessment methods might include continuous assessment, portfolio-based assessment, or real-world problem-solving tasks. These methods aim to evaluate a student’s practical skills and understanding, rather than just their ability to memorize information.
- Educational Management: This involves adopting new strategies for running educational institutions, like using data analytics to inform decision-making, implementing new models for student support services, or rethinking the way institutions are structured and governed.
The Human Element
At the core of educational innovation is the human element – understanding how students learn, what motivates them, and how educators can best support their learning journeys. It’s about creating an environment that is not only intellectually stimulating but also emotionally supportive and socially engaging.
The Role of Open Innovation
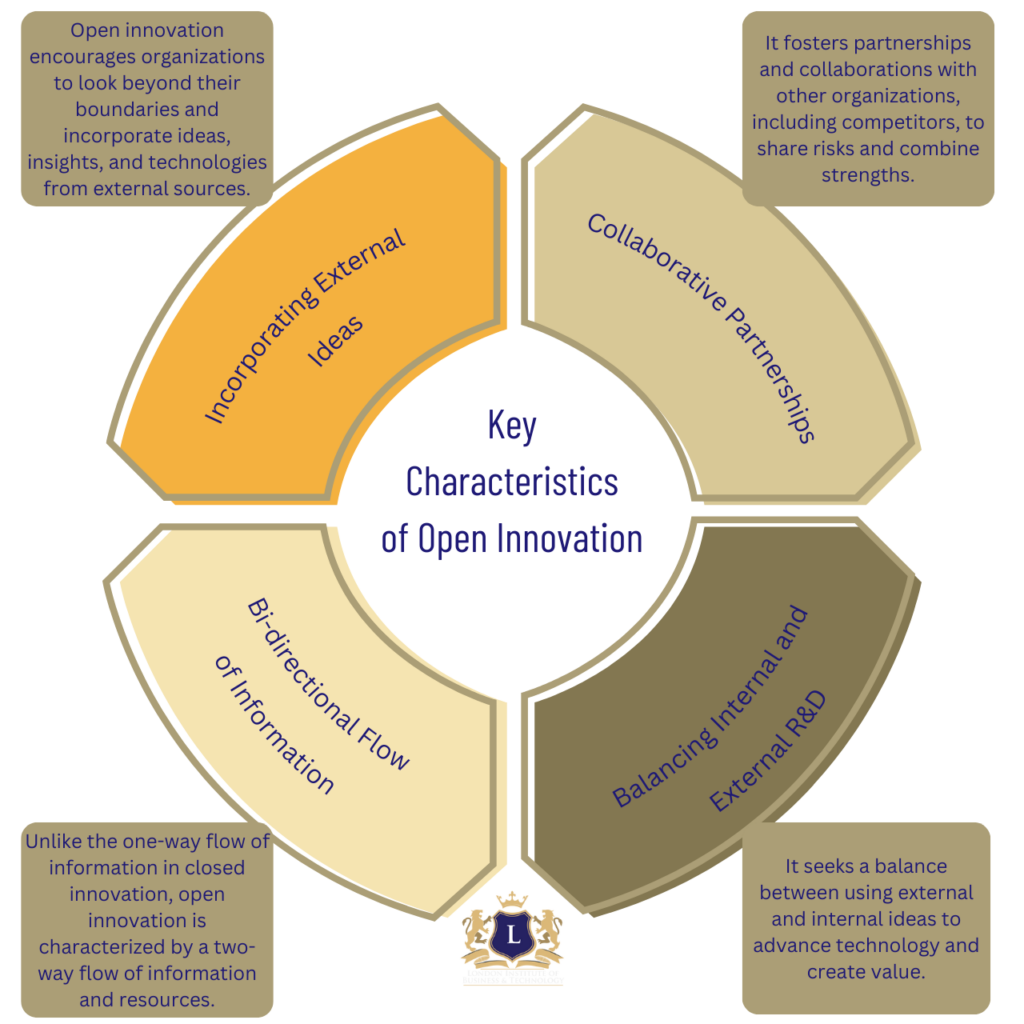
Open innovation, a term introduced by Henry Chesbrough, a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, in his 2003 book “Open Innovation: The New Imperative for Creating and Profiting from Technology,” represents a paradigm shift in how organizations approach innovation. Chesbrough’s concept of open innovation is a framework that challenges the conventional, closed model of innovation and proposes a more inclusive and outward-looking approach.
The Concept as Defined by Chesbrough
Chesbrough’s open innovation model suggests that organizations should utilize external as well as internal ideas and paths to market. This approach is in stark contrast to the traditional model of innovation, which emphasizes reliance solely on internal resources and capabilities. The closed model operates under the assumption that successful innovation requires control and secrecy, with a focus on internal research and development (R&D) leading to internally developed products and services.
Open Innovation in Higher Education
In the context of higher education, open innovation takes on a unique role. Universities and colleges are traditionally seen as hubs of knowledge creation, but they often operate within the confines of their institutional boundaries. Open innovation pushes these institutions to engage more dynamically with the external environment – including industry, government, and other educational institutions – to enhance their educational and research activities.
This approach in higher education can lead to:

Open innovation, as conceptualized by Henry Chesbrough, is not just a strategy for business but a transformative framework that can significantly impact the landscape of higher education, driving it towards more collaborative, relevant, and impactful horizons.
How do we do it?
At the LIKE Center, part of the London Institute of Business and Technology, the implementation of open innovation is a strategic process that involves several key steps and initiatives. These are designed to foster collaboration, encourage the exchange of ideas, and integrate external insights into the educational framework. Here’s how we do it:
1. Establishing Collaborative Networks
- Industry Partnerships: We actively seek partnerships with businesses and industry leaders. These partnerships can take various forms, from guest lectures and workshops to joint research projects. They provide students and faculty with insights into current industry practices and future trends.
- Academic Collaborations: Teaming up with other academic institutions, both domestically and internationally, allows for the exchange of ideas, research, and best practices in teaching methods.
2. Curriculum Co-Creation
- Involvement of Industry Experts: We involve professionals from relevant industries in curriculum development. This ensures that our courses are aligned with the latest industry needs and equip students with skills that are in high demand.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Regular feedback from students, alumni, and industry partners helps us continuously refine and update our curriculum.
3. Fostering a Culture of Innovation
- Innovation Labs and Workshops: The LIKE Center hosts innovation labs and workshops where students can work on real-world problems, often presented by our industry partners. This hands-on approach encourages creative problem-solving and practical learning.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship: We offer resources and support for students interested in entrepreneurship, including mentorship programs, networking events, and access to funding opportunities.
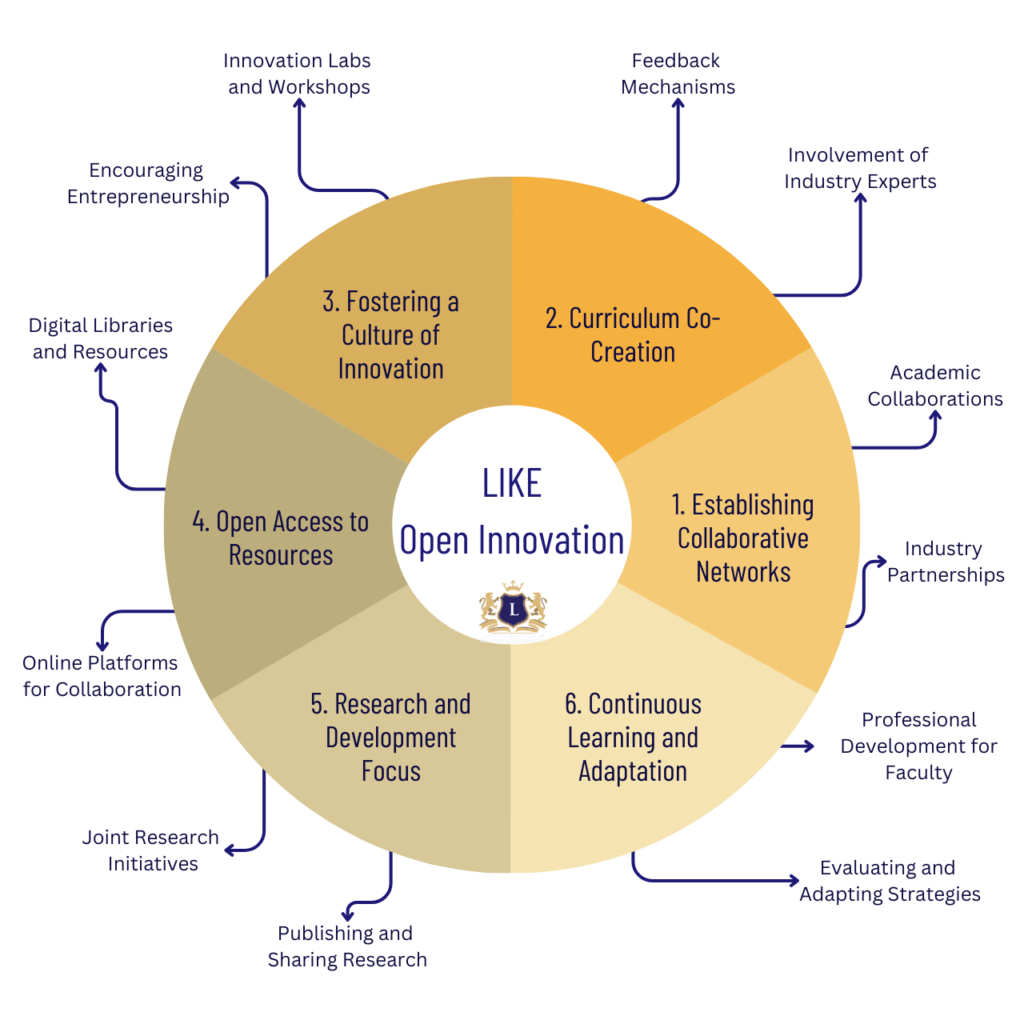
4. Open Access to Resources
- Digital Libraries and Resources: Providing students and faculty with access to a wide range of digital resources, including research papers, case studies, and e-books, encourages a broader understanding and integration of diverse knowledge.
- Online Platforms for Collaboration: Utilizing online platforms where students, faculty, and external experts can interact, share ideas, and work on projects together, even remotely.
5. Research and Development Focus
- Joint Research Initiatives: Engaging in research projects with external organizations not only enhances the practical relevance of our research but also provides additional funding and resources.
- Publishing and Sharing Research: We encourage open access publishing of research findings to contribute to the global pool of knowledge and foster wider collaboration.
6. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- Professional Development for Faculty: Regular training and development opportunities for faculty members ensure they stay abreast of the latest teaching methods and industry trends.
- Evaluating and Adapting Strategies: Regularly assessing the effectiveness of our open innovation strategies allows us to adapt and evolve in response to new challenges and opportunities.
By integrating these practices, we not only advance our educational offerings but also contribute to the broader ecosystem of innovation in higher education. This approach ensures that we remain at the forefront of educational excellence, preparing our students to be the innovators and leaders of tomorrow.







Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.